Physically speaking, DNA is a long string of paired chemical units (nucleotides) that come in four different types, abbreviated A, T, C, and G, and it carries information organized into units called genes. Genes typically provide instructions for making proteins, which give cells and organisms their functional characteristics.
Chromosome and Chromatid Number in Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet, PPT and PDF | Meiosis, Mitosis, Scientific method posters
Jul 31, 2022During DNA duplication in the S phase, each chromosome is replicated to produce two identical copies, called sister chromatids, that are held together at the centromere. The centrosomes, which are the structures that organize the microtubules of the meiotic spindle, also replicate. This prepares the cell to enter prophase I, the first meiotic

Source Image: album-online.com
Download Image
Fact Sheets about Genomics Chromosomes Fact Sheet En Español Chromosomes Fact Sheet Chromosomes are thread-like structures located inside the nucleus of animal and plant cells. What is a chromosome? Chromosomes are thread-like structures located inside the nucleus of animal and plant cells.
Source Image: thetech.org
Download Image
image008.jpg
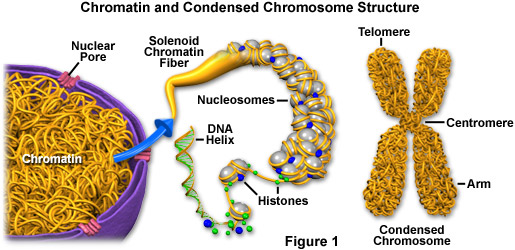
Each replicated chromosome consists of two sister chromatids. Chromosome centromeres serve as a place of attachment for spindle fibers during cell division. Metaphase: Chromatin becomes even more condensed and sister chromatids line up along the mid-region of the cell or the metaphase plate. Anaphase: Sister chromatids are separated and pulled
Source Image: biology.stackexchange.com
Download Image
How Many Chromatids Are In Each Replicated Chromosome
Each replicated chromosome consists of two sister chromatids. Chromosome centromeres serve as a place of attachment for spindle fibers during cell division. Metaphase: Chromatin becomes even more condensed and sister chromatids line up along the mid-region of the cell or the metaphase plate. Anaphase: Sister chromatids are separated and pulled
The role of mitosis in the cell cycle is to replicate the genetic material in an existing cell—known as the “parent cell”—and distribute that genetic material to two new cells, known as “daughter cells.” In order to pass its genetic material to the two new daughter cells, a parent cell must undergo cell division, or mitosis.
genetics – The human has 46 double chromosomes or simple chromosomes? – Biology Stack Exchange
A cell spends most of its life in interphase, which has three phases: G1, S, and G2. In the G1 phase, the cell grows and takes in nutrients. In the S phase, the cell’s DNA is replicated. Each replicated chromosome consists of two sister chromatids connected at the centromere. The G2 phase is another growth phase, after which the cell is ready
Duplicated Homologous Chromosomes Pair and Crossing-over Stock Vector | Adobe Stock | Cell division, Meiosis, Cell cycle

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
How many chromatids are in a chromosome? – Quora
A cell spends most of its life in interphase, which has three phases: G1, S, and G2. In the G1 phase, the cell grows and takes in nutrients. In the S phase, the cell’s DNA is replicated. Each replicated chromosome consists of two sister chromatids connected at the centromere. The G2 phase is another growth phase, after which the cell is ready
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Chromosome and Chromatid Number in Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet, PPT and PDF | Meiosis, Mitosis, Scientific method posters
Physically speaking, DNA is a long string of paired chemical units (nucleotides) that come in four different types, abbreviated A, T, C, and G, and it carries information organized into units called genes. Genes typically provide instructions for making proteins, which give cells and organisms their functional characteristics.

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
image008.jpg
Fact Sheets about Genomics Chromosomes Fact Sheet En Español Chromosomes Fact Sheet Chromosomes are thread-like structures located inside the nucleus of animal and plant cells. What is a chromosome? Chromosomes are thread-like structures located inside the nucleus of animal and plant cells.

Source Image: sas.upenn.edu
Download Image
Chromosomes/chromatids
Jul 13, 2023Each chromosome in the sister chromatid structure represents one chromatid. Figure 8.4. 3: Diagram of Replicated and Condensed Eukaryotic Chromosome (sister chromatids). (1) Chromatid – one of the two identical parts of the chromosome after S phase. (2) Centromere – the point where the two chromatids are joined together.
Source Image: vcbio.science.ru.nl
Download Image
Harlequin chromosomes, light micrograph – Stock Image – C057/5344 – Science Photo Library
Each replicated chromosome consists of two sister chromatids. Chromosome centromeres serve as a place of attachment for spindle fibers during cell division. Metaphase: Chromatin becomes even more condensed and sister chromatids line up along the mid-region of the cell or the metaphase plate. Anaphase: Sister chromatids are separated and pulled

Source Image: sciencephoto.com
Download Image
Meiosis, inheritance and variation — Science Learning Hub
The role of mitosis in the cell cycle is to replicate the genetic material in an existing cell—known as the “parent cell”—and distribute that genetic material to two new cells, known as “daughter cells.” In order to pass its genetic material to the two new daughter cells, a parent cell must undergo cell division, or mitosis.

Source Image: sciencelearn.org.nz
Download Image
How many chromatids are in a chromosome? – Quora
Meiosis, inheritance and variation — Science Learning Hub
Jul 31, 2022During DNA duplication in the S phase, each chromosome is replicated to produce two identical copies, called sister chromatids, that are held together at the centromere. The centrosomes, which are the structures that organize the microtubules of the meiotic spindle, also replicate. This prepares the cell to enter prophase I, the first meiotic
image008.jpg Harlequin chromosomes, light micrograph – Stock Image – C057/5344 – Science Photo Library
Jul 13, 2023Each chromosome in the sister chromatid structure represents one chromatid. Figure 8.4. 3: Diagram of Replicated and Condensed Eukaryotic Chromosome (sister chromatids). (1) Chromatid – one of the two identical parts of the chromosome after S phase. (2) Centromere – the point where the two chromatids are joined together.